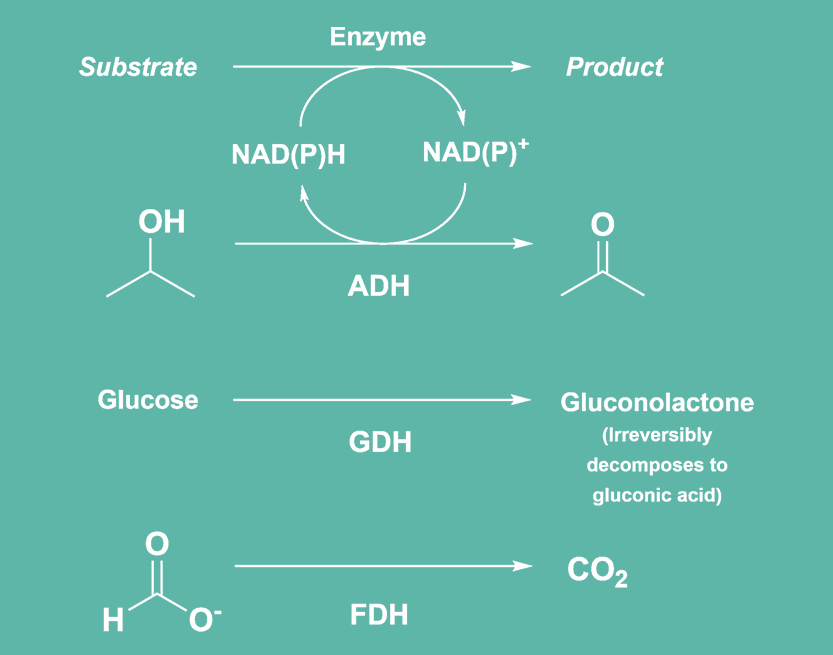
Cofactor regeneration enzyme technology
Many enzymes used as biocatalysts require NAD(P)+ to facilitate oxidation-reduction reactions. To be able to use this cofactor in catalytic amounts, the oxidised cofactor must be continuously reduced, this is called cofactor regeneration. The enzymes accept either or both NAD(P)+ cofactors and their regeneration can be achieved by adding a cofactor regeneration enzyme (GDH, FDH, or ADH), and its substrate (D-glucose, sodium formate, or isopropanol).