Glucose dehydrogenase enzyme technology
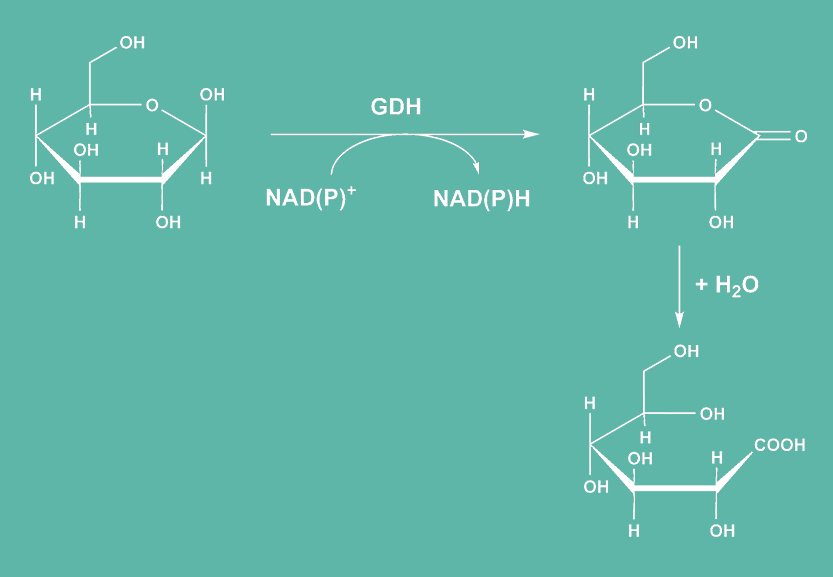
Glucose dehydrogenase (GDH enzymes) catalyses the oxidation of D-glucose to D-glucolactone, while reducing in turn NAD+ or NADP+ to NADH and NADPH. The product of this reaction, D-glucolactone, spontaneously and irreversibly hydrolyses in water to gluconic acid, which favors the formation of reduced NADH and NADPH.
Advantages of using glucose dehydrogenase:
- GDH enzyme is an efficient system for cofactor regeneration owing to its cheap substrate, the favourable reaction equilibrium towards the reduced cofactor and the high activity of the enzyme.
- Easily scalable technology due to the GDH enzyme stability in a wide range of reaction conditions.