Rhodium’s high melting point, high temperature stability and corrosion resistance properties make it a key component in vehicle emission control, as well as glass production and chemical catalysts.
Rhodium uses
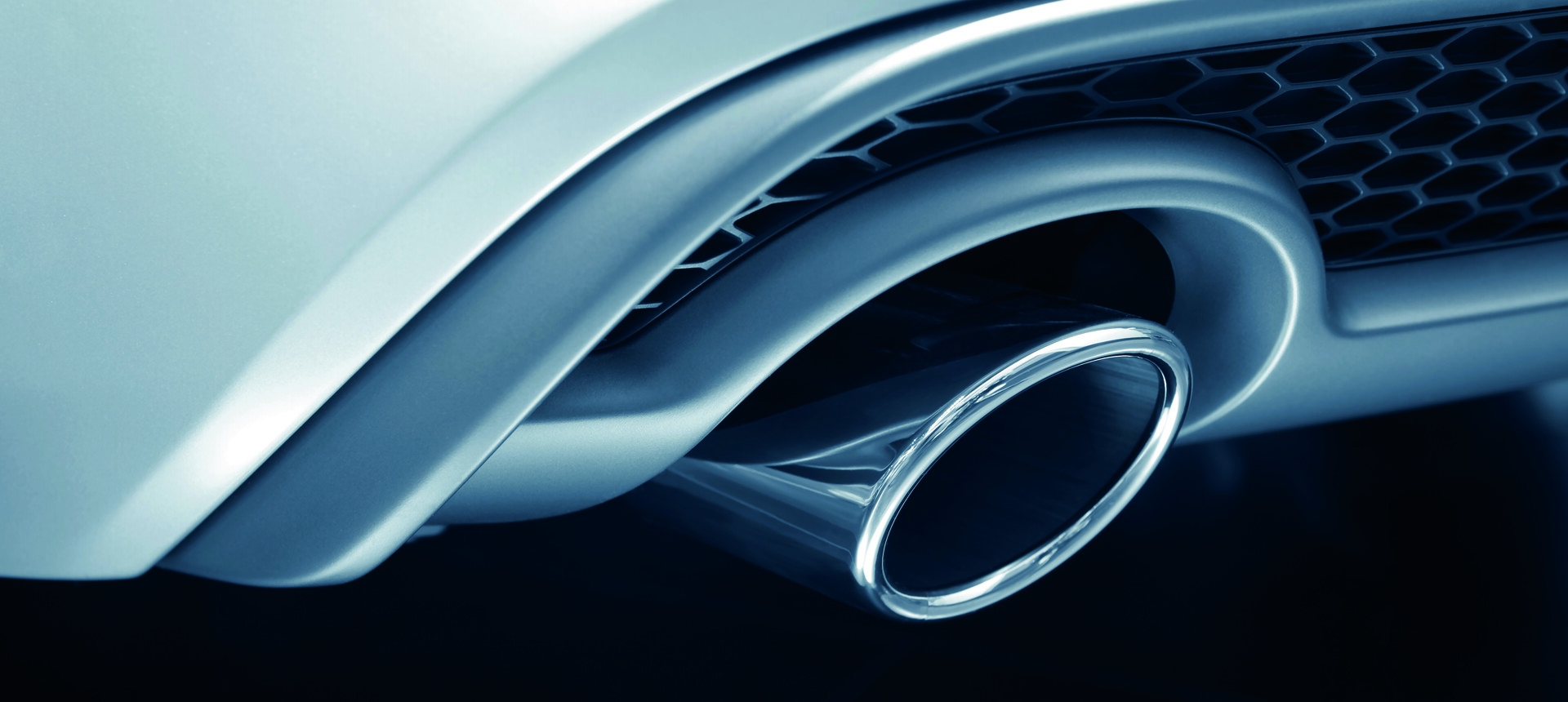
Rhodium’s largest use is found in the automotive emissions control market. Rhodium’s selectivity and control of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and its tolerance to poisons in the exhaust, make it critical in gasoline-fueled vehicles and unrivalled by any other metal.
Outside the automotive industry, rhodium has applications in two other main markets. Because of rhodium’s high melting point, it is used in platinum-rhodium alloys to increase durability in glassmaking applications. Higher rhodium content in the alloy allows equipment to better withstand high temperatures, allowing for longer durability.
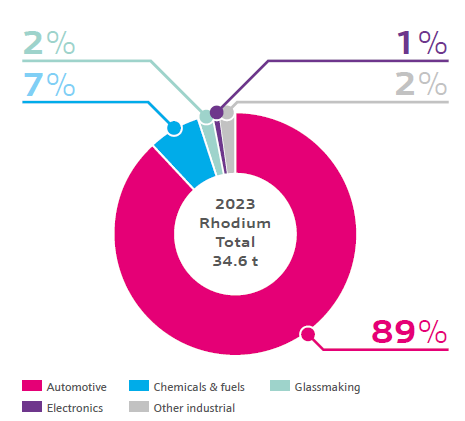

In the chemical industry, rhodium is mainly used as a catalyst to produce acetic acid, a bulk commodity chemical used to make other products, and oxo-alcohol products, used as plasticisers.




