Selective Catalytic Reduction Filter® (SCRF®)
Johnson Matthey’s SCRF® system integrates selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology coated on a diesel particulate filter (DPF). SCRF plays a key role in modern diesel after-treatment systems to control both oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions.
In a lean gas stream, it is necessary to add a reductant such as ammonia to the system to enable this reaction. Ammonia-SCR systems react ammonia (NH3) with the NOx to form nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O). There are three reaction pathways:
4NH3 + 4NO + O2 → 4N2 + 6H2O
2NH3 + NO + NO2 → 2N2 + 3H2O
8NH3 + 6NO2 → 7N2 + 12H2O
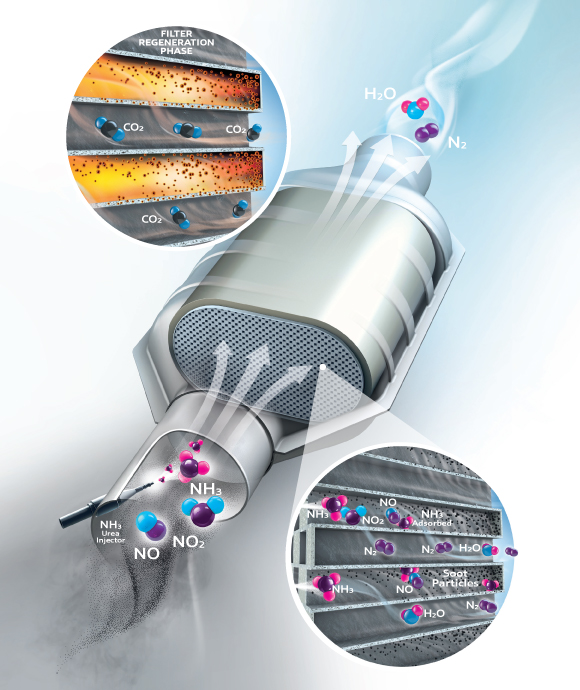
Any source of ammonia can be used, but most commonly the source is an aqueous solution of urea. This decomposes in the exhaust stream in two stages to form ammonia and carbon dioxide (CO2):
NH2C(O)NH2 → HNCO + NH3
↓
HNCO + H2O → CO2 + NH3
Composition: Typically, Cu-Zeolite coated onto a filter substrate.
Our selective catalytic reduction filters…
- Have market-leading Cu-Zeolite washcoat technology to deliver advanced NOx emissions control.
- Are tailored to customers’ individual systems.
- Help enable our customers to meet increasingly stringent NOx and PN legislation aspects.
- Are highly durable against temperatures and poisons.
- Are being developed to help catalyst after-treatment systems achieve low N2O emissions, supporting future legislation requirements.

