Ruthenium is considered one of the earth's rarest metals. Its unique properties are particularly useful in electronic and electrochemical industrial applications.
Ruthenium uses
The electronics industry uses ruthenium for chip components, hard disk drives and electrical contacts requiring high wear resistance. Ruthenium oxide-based ceramic paste is used in resistor components, which are present in almost every chip device, hybrid integrated circuitry and arrays.
Computer hard disk drive memory using ruthenium as an underlayer to its platinum-containing storage layer has enabled data storage density to greater increase.
Ruthenium is also widely used in electrochemical applications because of its wear resistance. Examples include:
- a coating on electrodes for chloro-alkali production
- electrocatalyst in gas diffusion electrodes (Ruthenium black)
- salt-water chlorination of swimming pools
- electrochemical treatment of shipping ballast water to kill invasive species
- often used in electrolysis with iridium.
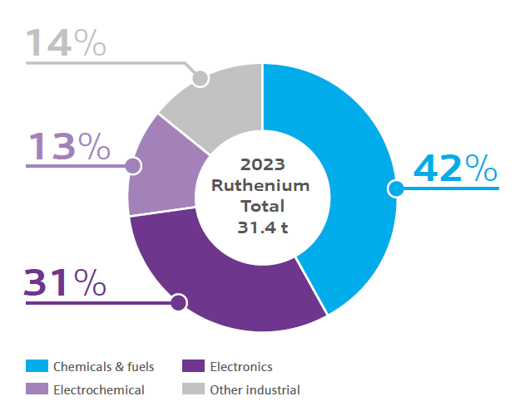

In the chemical industry, ruthenium catalysts are used:
- as a catalyst in China to make caprolactam - a precursor to nylon
- in acetic acid production
- in catalytic wet air oxidation for the treatment of industrial wastewater.
Ruthenium alloys can be found in extremely hard tungsten carbide alloys used in the machine tool industry. It is also found in corrosion-resistant alloys for the oil, gas and chemicals industries. There is increasing interest in ruthenium for energy-transition applications particularly in the hydrogen economy.

PGM chemical and catalysts products
Learn more about our full range of product offerings for Ru chemicals and catalyst products.